IVC Leads are little cone-formed clinical gadgets that are embedded in the sub-par vena cava, which is the primary vein that pushes platelets from the lower furthest points, for example, the foot, lower legs, knees, and hips, to the heart and lungs.
Regularly, a vascular specialist or interventional radiologist embeds the channel so as to forestall blood clusters from climbing the vena cava to the lungs. This occasionally dangerous circumstance is known as an aspiratory embolism (PE).
For the most part, IVC channels are created from non-attractive materials that are additionally non-ferromagnetic. This permits patients to experience a X-ray assessment without issue, which confirms the area and viability of the gadget inside the human body.
Another distinctive element incorporates the legs, or swaggers, which join to the internal dividers of the vena cava.
IVC channels have the accompanying characteristics:
- Planned from biocompatible and non-destructive substances
- Ought not move, tilt, tear, or crack while inside the vena cava
- Ought to be made out of non-ferromagnetic substances to permit a X-ray
- By and large, isn’t perpetual, hence ought to be retrievable
- Ought to be intended for simple implantation
- Ought to contain most blood clumps to the point it can forestall a PE
- Has caval patency, which is the point at which the channel is “open” and prevents blood from coagulating upon contact with the channel. This is additionally called non-thrombogenic
- Shape and structure ought to oversee after some time
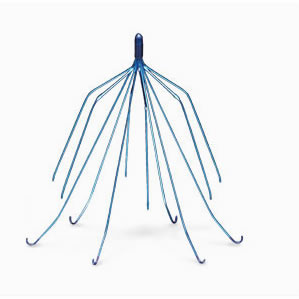

As indicated by the MAUDE database the time this was composed, the two channels that saw the most elevated number of grumblings was the Versifier Recuperation and Minstrel G2.
Dr. Williamson from York Emergency clinic in Pennsylvania led an investigation on 80 patients tending to cracking and embolization of the Recuperation and G2. The outcomes were upsetting. 25% (7 out of 28) patients embedded with the G2 encountered these issues. Following a fluoroscopy, 16% found in any event one swagger from the channel had broken after 37.8 months of its implantation.
Dr. Williamson inferred that more than 7,000 U.S. patients could have a cracked Minstrel G2, which has been demonstrated that channel sections that movement to an organ could be lethal. Parts could likewise migrate to the hepatic vein or lung.
As indicated by Dr. Williamson, “In light of the fact that nitinol metal exhaustion may assume a job in the channel break, it is sensible to accept the occurrence of channel crack would be straightforwardly corresponding to the time that the channel is permitted to abide in the patient after implantation.”

